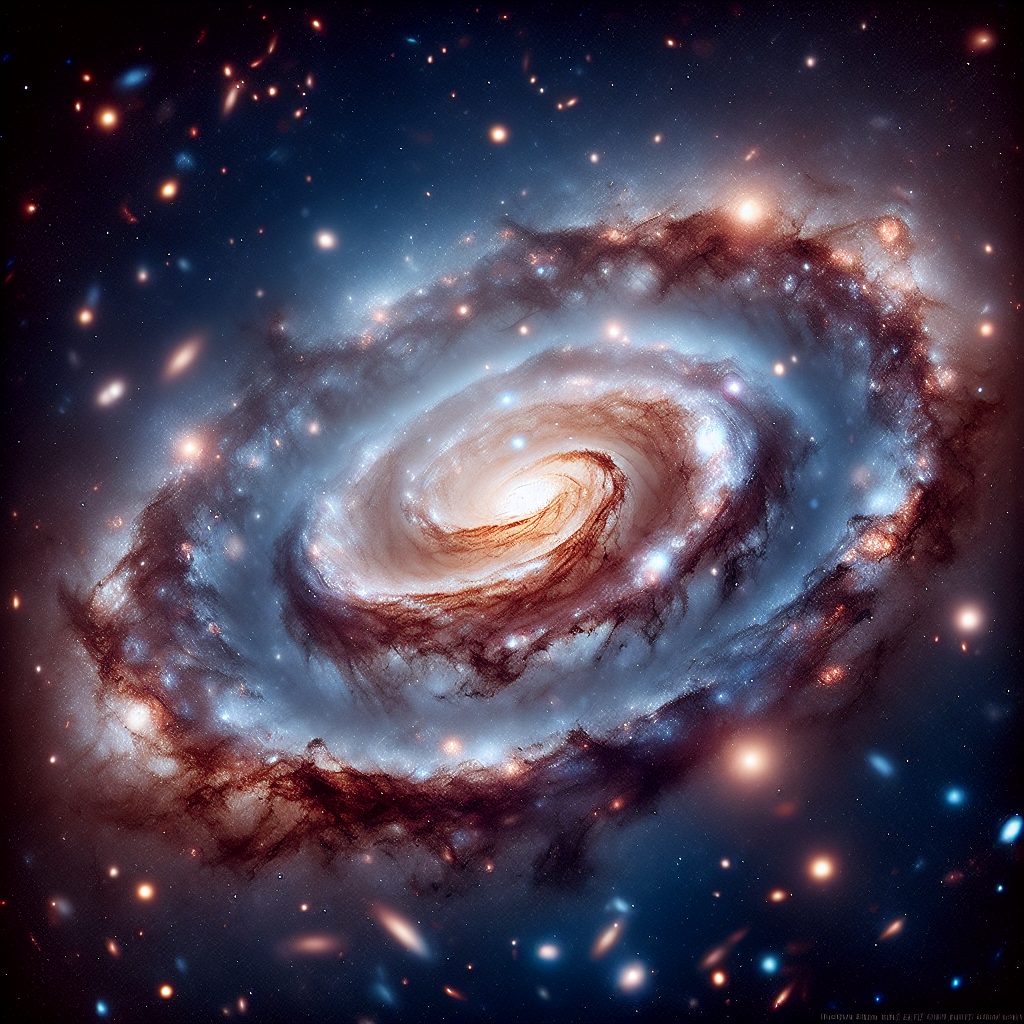
In a groundbreaking development for the field of astrophysics, researchers have confirmed the existence of a galaxy composed almost entirely of dark matter, as reported by Wired in their article titled “A Galaxy Composed Almost Entirely of Dark Matter Has Been Confirmed.” This discovery offers a new frontier in understanding the universe’s most enigmatic components.
The galaxy in question, known as FAST J0139+4328, is situated hundreds of millions of light-years away from Earth. Its dominance in dark matter has puzzled scientists since its first tentative identification. Unlike typical galaxies, where visible matter such as stars and gas clusters define their structure, this galaxy defies traditional interpretations, with dark matter making up approximately 99.99% of its composition.
The significance of this discovery cannot be overstated. Dark matter, an elusive material that does not emit, absorb, or reflect light, has remained one of the most perplexing components known to science. It is believed to account for about 85% of the universe’s total mass. Despite its prevalence, it interacts so weakly with ordinary matter that its presence can only be inferred through gravitational effects on visible matter, a process that had previously limited detection primarily to indirect observations.
According to the original report in Wired, the research team, led by experts in the field of astrophysics, utilized a combination of state-of-the-art radio telescopes, optical telescopes, and theoretical models to confirm the galaxy’s characteristics. The findings challenge existing models of galaxy formation and evolution and suggest that our understanding of cosmic structures may require significant revisions.
This galaxy’s discovery provides a unique laboratory to study the properties of dark matter in an environment where it is overwhelmingly dominant. Such studies have the potential to unveil the role dark matter plays in galaxy formation and its contribution to the universe’s large-scale structure. Researchers hope that by understanding how a galaxy like FAST J0139+4328 can exist virtually devoid of visible matter, they might unlock new insights into the fundamental nature of dark matter itself.
Moreover, this confirmation of a dark matter-dominated galaxy highlights the advanced capabilities of modern astronomical technology. The integration of next-generation telescopes and sophisticated computational models is crucial in pushing the boundaries of what can be observed and understood about the universe.
The implications of this discovery extend beyond the academic realm, potentially influencing future research and development in areas such as cosmology and particle physics. As scientists continue to explore the mysteries that galaxies like FAST J0139+4328 present, the ongoing quest to unravel the universe’s dark matter puzzle remains at the forefront of scientific inquiry.
In conclusion, the confirmation of a galaxy composed almost entirely of dark matter signifies a pivotal moment in astrophysics, opening new pathways for research and understanding. This discovery marks a step closer to unlocking one of the cosmos’ most profound mysteries, as the scientific community continues to probe the depths of the universe in pursuit of knowledge.